'Rcpp' implementation of the geomorphon terrain classification system based on 'r.geomorphon' algorithm of Jasiewicz and Stepinski (2013) from 'GRASS GIS'.
Usage
geomorphons(
elevation,
filename = NULL,
search = 3,
skip = 0,
flat_angle_deg = 1,
dist = 0,
comparison_mode = "anglev1",
tdist = 0,
forms = TRUE,
ternary = FALSE,
positive = FALSE,
negative = FALSE,
use_meters = FALSE,
nodata_val = NA_integer_,
xres = NULL,
yres = xres,
simplify = FALSE,
LAPPLY.FUN = lapply,
nchunk = geomorphon_chunks_needed(elevation)
)Arguments
- elevation
matrix or SpatRaster object. Digital Elevation Model values. It is STRONGLY recommended to use a grid in a projected coordinate system.
- filename
character. Output filename. Default
NULLcreates a temporary file.- search
numeric. User input for search radius (default:
3). Units depend onuse_meters.- skip
numeric. User input for skip radius (default:
0). Units depend onuse_meters.- flat_angle_deg
numeric. Flatness angle threshold in degrees. Default:
1.0.- dist
numeric. Flatness distance (default:
0). Units depend onuse_meters.- comparison_mode
Character. One of
"anglev1","anglev2","anglev2_distance". Default:"anglev1".- tdist
numeric. Terrain distance factor. When greater than 0, overrides Z tolerance from angular logic. Default:
0.0.- forms
character. Number of geomorphon forms to identify. One of
"forms10(default),"forms6","forms5", or"forms4.- ternary
logical. Include "ternary" output? Default:
FALSE- positive
logical. Include "positive" output? Default:
FALSE- negative
logical. Include "negative" output? Default:
FALSE- use_meters
Logical. Default:
FALSEuses cell units. Set toTRUEto specifysearch,skip, anddistin units of meters.- nodata_val
numeric. NODATA value. Default:
NA_integer_.- xres
numeric. X grid resolution (used only when
elevationis a matrix). Default:NULL.- yres
numeric. Y grid resolution (used only when
elevationis a matrix). Default:xres.- simplify
logical. If result is length
1list, the first element is returned. Default:FALSE- LAPPLY.FUN
An
lapply()-like function such asfuture.apply::future_lapply(). Default:lapply().- nchunk
Number of tile chunks to use. Default:
geomorphon_chunks_needed(elevation).
Value
List of SpatRaster or matrix of geomorphon algorithm outputs. When
more than one of forms, ternary, positive, negative are set the
result is a list. For one result type, and default simplify argument, the
result is the first (and only) element of the list.
Distance Calculation and Coordinate Reference Systems
The algorithm assumes planar distances and angles are calculated based on cell resolutions, so it is strongly recommended that elevation data be in a projected coordinate system.
Buffer Around Area of Interest
For reliable geomorphon classification, especially near study area
boundaries, it is recommended to use a raster that includes a buffer of at
least search + 1 cells around the area of interest. This implementation
utilizes all available DEM data up to the specified search radius.
A buffer of search + skip + 1 cells is automatically applied when
processing SpatRaster input, as this is necessary to avoid edge effects when
processing large rasters in tiles. Matrix input is not altered.
Tiled Processing for Large Rasters
For Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) that are too large to fit into available
memory, rgeomorphon employs an automatic tiled processing workflow. This
method breaks the large raster into a grid of smaller, manageable chunks that
are processed sequentially.
The premise of this approach is the use of buffered tiles. To ensure seamless results and avoid edge artifacts, a buffer of surrounding data is added to each chunk before the geomorphon calculation is performed. This provides the necessary neighborhood of cells for the algorithm to work correctly. After each tile is processed, the buffer region is removed from the result. Finally, the clean, processed tiles are mosaicked back together into a single, complete output raster that perfectly matches the extent of the original input DEM.
This entire workflow is handled internally by the main geomorphons()
function, which can also leverage parallel processing to speed up the
operation on multi-core systems. See the vignette on parallel processing with
'future' package.
The number of chunks needed can be controlled by setting several environment variables. These variables are read by the function at runtime.
Default Behavior
By default, the function assumes a single worker, scales the estimated memory needed by a factor of 10, and applies the square root to the total number of chunks. This can be replicated with the following settings:
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_N_WORKERS = 1)
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_MEM_SCALE_NEED = 10)
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_MEM_SCALE_WORKERS = 1)
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_MEM_POWER = 0.5)Customized Behavior
You can customize the tiling behavior by setting the environment variables to different values. For example, to use four workers, scale memory needs by a factor of five, apply a worker scaling factor of two, and a power of 1.5 to the total, you would set the following:
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_N_WORKERS = 4)
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_MEM_SCALE_NEED = 5)
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_MEM_SCALE_WORKERS = 2)
Sys.setenv(R_RGEOMORPHON_MEM_POWER = 1.5)Comparison with 'GRASS' 'r.geomorphon'
This implementation achieves very high agreement with the classification logic of 'GRASS GIS' 'r.geomorphon' when using equivalent parameters and data in a projected coordinate system.
'r.geomorphon' employs a row buffering strategy which can, for cells near the edges of a raster, result in a truncated line-of-sight compared to the full raster extent. This may lead GRASS to classify edge-region cells differently or as NODATA where this implementation may produce a more 'valid' geomorphon form given the available data.
More information about the 'r.geomorphon' module can be found in the GRASS GIS manual: https://grass.osgeo.org/grass-stable/manuals/r.geomorphon.html
References
Stepinski, T., Jasiewicz, J., 2011, Geomorphons - a new approach to classification of landform, in : Eds: Hengl, T., Evans, I.S., Wilson, J.P., and Gould, M., Proceedings of Geomorphometry 2011, Redlands, 109-112. Available online: https://www.geomorphometry.org/uploads/pdf/pdf2011/StepinskiJasiewicz2011geomorphometry.pdf
Jasiewicz, J., Stepinski, T., 2013, Geomorphons - a pattern recognition approach to classification and mapping of landforms, Geomorphology, vol. 182, 147-156. (doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.11.005 )
Examples
library(terra)
library(rgeomorphon)
SEARCH = 7 # outer search radius (cells)
SKIP = 1 # inner skip radius (cells)
DIST = 0 # flatness distance (cells)
FLAT = 1 # flat angle threshold
MODE = "anglev1" # comparison mode
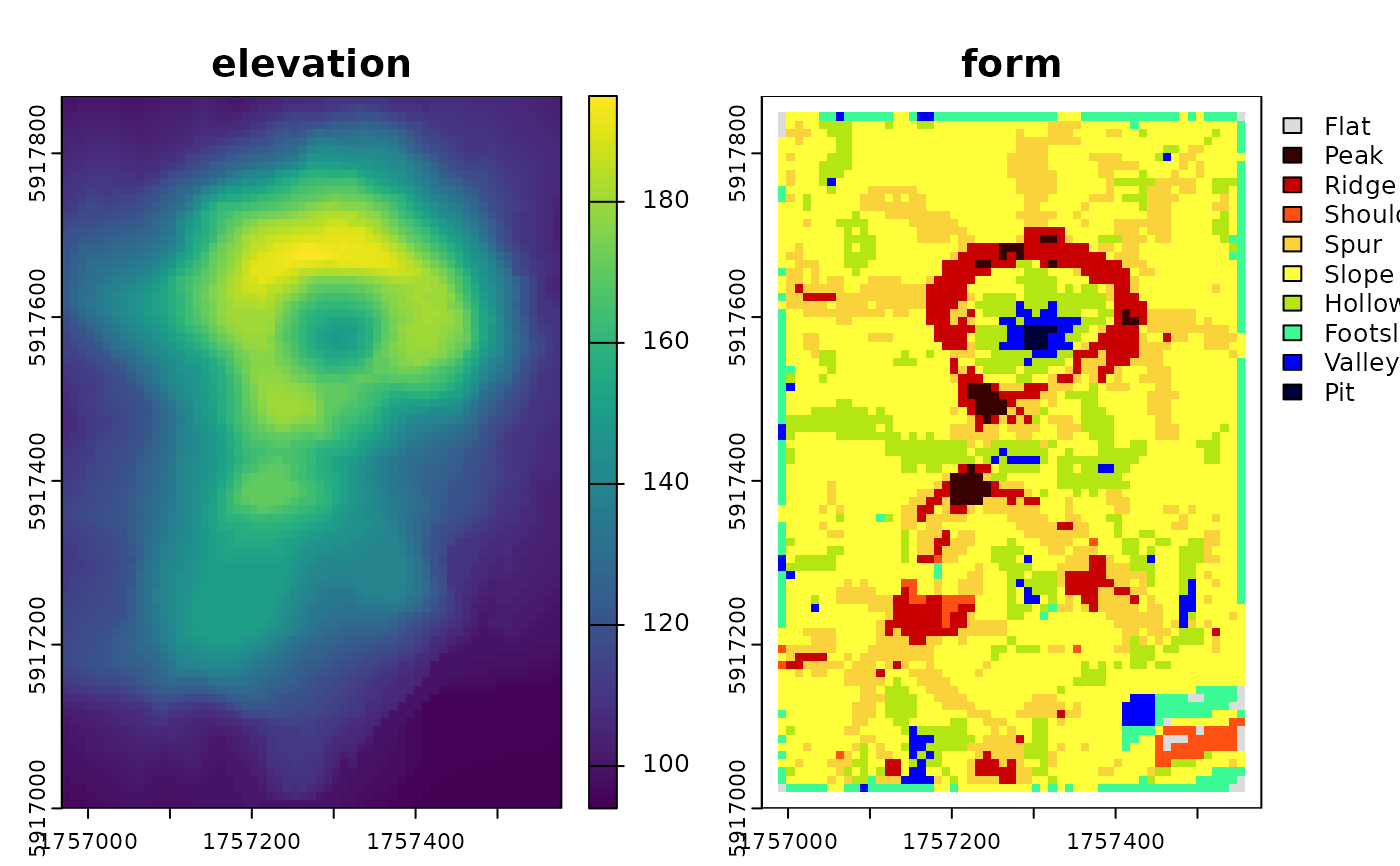
## classic volcano
data("volcano", package = "datasets")
dem <- terra::rast(volcano)
terra::crs(dem) <- terra::crs("EPSG:2193")
terra::ext(dem) <- c(1756968, 1757578, 5917000, 5917870)
names(dem) <- "elevation"
system.time({
rg <- geomorphons(
dem,
search = SEARCH,
skip = SKIP,
dist = DIST,
flat = FLAT,
comparison_mode = MODE
)
})
#> user system elapsed
#> 0.040 0.000 0.033
plot(c(dem, rg))